Introduction:
When it comes to powering machines and equipment, electric motors play a crucial role. Two of the most common types are AC Motor and DC Motor. Each type has its unique advantages and applications, making it essential to understand their differences before deciding which is right for your specific needs. In this article, I’ll dive deep into the AC Motor vs DC Motor: advantages, disadvantages, workings and applications of both AC and DC motors.
To clear all the concepts and doubts on AC Motor vs DC Motor first we need to understand AC motors then we move on DC motors.
1. Understanding DC Motors
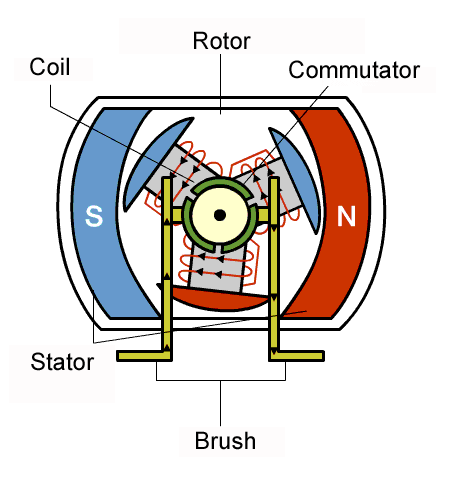
1.1 How DC Motors Work
DC motors operate on direct current (DC) electricity. In DC motors, electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy through the interaction of a current-carrying conductors and magnetic field. The components include a rotor (rotating part), a stator (stationary part), and a commutator that switches the current direction to maintain rotational motion.
1.2 Types of DC Motors
- Brushed DC Motors: It contains a commutator and brushes to control the current direction. They are simple, cost-effective, and easy to control but require regular maintenance.
- Brushless DC Motors: In these motors the electronic controllers used instead of brushes, offering higher efficiency, lower maintenance, and longer lifespan.
1.3 Advantages of DC Motors
High Starting Torque: Ideal for applications requiring a strong initial force.
Precise Speed Control: Easier to control speed with a wide range of adjustability.
Simpler Control Mechanisms: DC motors are generally easier to control with simple circuits.
1.4 Disadvantages of DC Motors
Maintenance Requirements: Brushed DC motors need frequent maintenance due to wear on brushes and commutators.
Limited Lifespan: Limited Lifespan: Over time, the mechanical parts of brushed motors deteriorate.
Higher Costs: Generally more expensive than AC motors of equivalent power output.
2. Understanding AC Motors
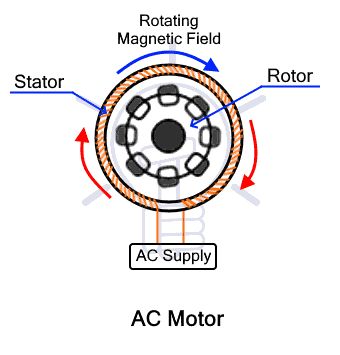
2.1 How AC Motors Work
AC motors operate on alternating current (AC) electricity. The rotor of an AC motor rotates because of the magnetic field created by the alternating current. The components including the rotor, stator, slip ring and commutator for specific types of AC motors.
2.2 Types of AC Motors
- Induction Motors: The most common type of AC motor, where the rotor is induced by the magnetic field in the stator. These motors are reliable, rugged and widely used in industrial applications.
- Synchronous Motors: These motors operate at a constant speed regardless of the load and are used where precise timing is essential.
- Servo Motors: High-performance motors used in precision control applications like robotics.
2.3 Advantages of AC Motors
Low Maintenance: Induction motors are less likely to wear down since they have less moving parts.
Cost-Effective: Generally cheaper and more readily available than DC motors.
Wide Availability: AC power is more commonly available, making AC motors easier to use in most settings.
2.4 Disadvantages of AC Motors
Complex Speed Control: Controlling the speed of AC motors typically requires more complex systems like variable frequency drives (VFDs).
Lower Starting Torque: AC motors usually have a lower starting torque compared to DC motors.
Power Factor Issues: Some AC motors, particularly induction motors, can suffer from power factor issues, which may require correction.
3. Differences Between DC and AC Motors (AC Motor vs DC Motor)
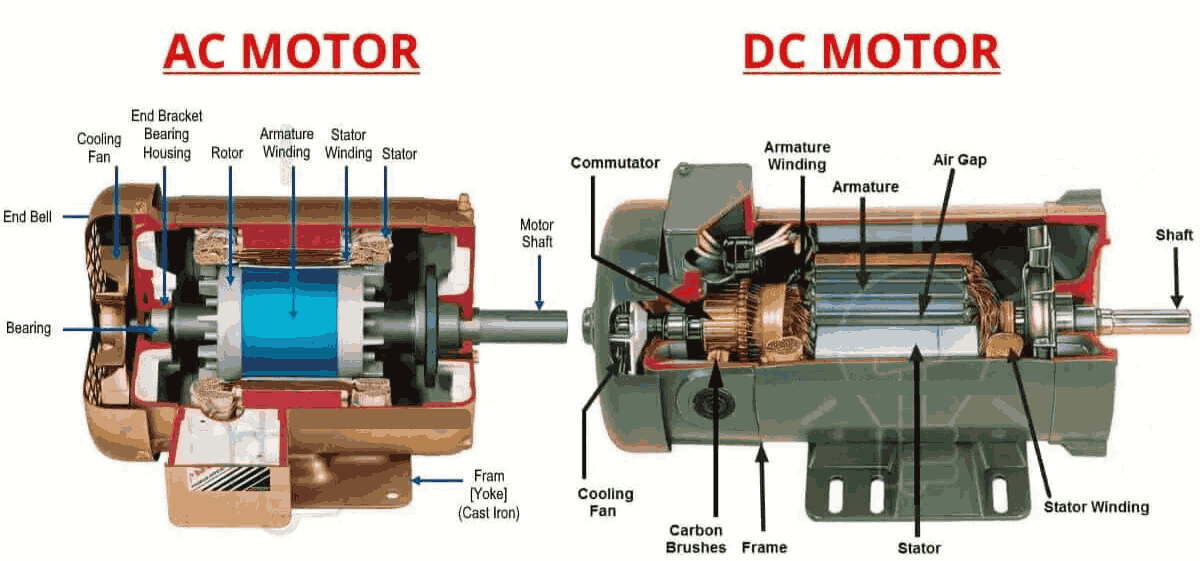
3.1 Power Supply
DC Motors: Operate on direct current, which is unidirectional and constant.
AC Motors: Operate on alternating current, where the flow of electricity periodically reverses direction.
3.2 Speed Control
DC Motors: Offer more straightforward and precise speed control, making them ideal for applications where speed variation is crucial.
AC Motors: Require more sophisticated control systems like VFDs for speed variation, making them slightly more complex to manage.
3.3 Efficiency and Performance
DC Motors: Generally more efficient at converting energy into mechanical motion, especially in applications requiring high torque at low speeds.
AC Motors: While less efficient in some scenarios, they are more suitable for constant speed applications and can handle higher power loads.
3.4 Applications
DC Motors: Commonly used in electric vehicles, elevators, conveyor belts, and other applications requiring precise speed control and high starting torque.
AC Motors: Widely used in industrial machinery, HVAC systems, household appliances, and large-scale equipment where efficiency and durability are key.
AC Motor vs DC Motor
| Feature |
AC Motor |
DC Motor |
| Type of Current |
Alternating Current (AC) |
Direct Current (DC) |
| Magnetic Field |
Alternating (changes direction periodically) |
Steady/Unidirectional (constant direction) |
| Magnets Used |
Primarily electromagnets (temporary magnetic field) |
Often uses permanent magnets in the stator (constant magnetic field) combined with electromagnets in the rotor |
| Rotor Interaction |
Rotor magnetic field induced by the stator’s rotating magnetic field |
Rotor magnetic field generated directly by current flowing through windings |
| Speed Control |
Controlled by varying the frequency of the AC supply |
Controlled by varying the voltage or using resistors |
| Efficiency at Low Speeds |
Less efficient at low speeds, typically used in high-speed applications |
More efficient at low speeds, making it suitable for applications requiring precise control |
| Construction Complexity |
Generally simpler, with fewer components |
More complex, especially with the inclusion of commutators and brushes in traditional designs |
| Maintenance |
Low maintenance due to lack of brushes (in most types) |
Higher maintenance due to brushes and commutators in traditional DC motors |
| Common Applications |
Household appliances, industrial machines, HVAC systems |
Electric vehicles, robotics, small tools, and applications requiring precise speed control |
4. Choosing the Right Motor
4.1 Factors to Consider
When choosing between a DC motor and an AC motor, consider the following factors:
Power Source Availability: If AC power is readily available, an AC motor might be more convenient.
Speed Control Needs: If your application requires precise and variable speed control, a DC motor may be the better choice.
Cost and Maintenance: Consider the long-term maintenance and initial cost. AC motors are mostly more affordable and require less maintenance.
Torque Requirements: If high starting torque is necessary, a DC motor might be more suitable.
4.2 Example Applications
DC Motor Applications: Electric vehicles, cranes, and robotics.
AC Motor Applications: Industrial pumps, fans, blowers, and compressors.
Conclusion:
In colclusion of AC motor vs DC motor, both DC and AC motors have their distinct advantages and are suitable for different types of applications. Understanding the key differences in their operation, performance, and maintenance requirements will help you make an informed decision. Whether you need precise speed control, high starting torque, or a reliable motor for industrial use, there’s a motor type that fits your needs.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference in AC Motor vs DC Motor?
The main difference in AC Motor vs DC Motor is the current they use: AC motors run on alternating current, while DC motors run on direct current.
2. Are AC motors cheaper than DC motors?
Yes, AC motors are typically less expensive and more widely available than DC motors.
3. Can high-torque applications be implemented with AC motors?
While AC motors can be used for high-torque applications, DC motors are generally preferred for situations where high starting torque is required.
4. Which motor is better for speed control AC motor or DC motor?
Generally, When we talk about AC motor vs DC motor, the DC motors perform better in applications that need for accurate and variable speed control.
5. What are some common applications for DC motors?
DC motors are commonly used in electric vehicles, elevators, and conveyor systems.

 Cloud computing is a technology that provides us with virtual resources over the internet.
Cloud computing is a technology that provides us with virtual resources over the internet.











 Gbps, thanks to its Super speed transfer mechanism. Additionally, to set itself apart from the previous USB 2.0 standard, it featured a stylish blue port design.
Gbps, thanks to its Super speed transfer mechanism. Additionally, to set itself apart from the previous USB 2.0 standard, it featured a stylish blue port design. The naming of every preceding generation is now adjusted retrospectively to reflect the new name. In this way, USB 3.1 evolved into USB 3.1 Gen 2 and USB 3.0 into USB 3.1 Gen 1. With the release of USB 3.2 in 2017, these names underwent yet another modification.
The naming of every preceding generation is now adjusted retrospectively to reflect the new name. In this way, USB 3.1 evolved into USB 3.1 Gen 2 and USB 3.0 into USB 3.1 Gen 1. With the release of USB 3.2 in 2017, these names underwent yet another modification.