Variable Speed Electric Motors
Introduction:
Variable speed electric motors are some of the most needed and common electric motors used in industries today. These motors are anticipated to run at speeds, to enable their control and optimal efficiency in terms of energy usage. The objective of this article is to discuss the working principle, components, types of winding, and modes of operation of variable speed electric motors.
Working Principle:
Variable speed electric motors utilize electromagnetic induction as their mode of operation. In this case, when an electrical current is passed through the motor’s windings, it produces a magnetic field, hence rotating the rotor. Therefore, for different applications, the speed of the motor can be controlled according to the required frequency and voltage of the electrical input.
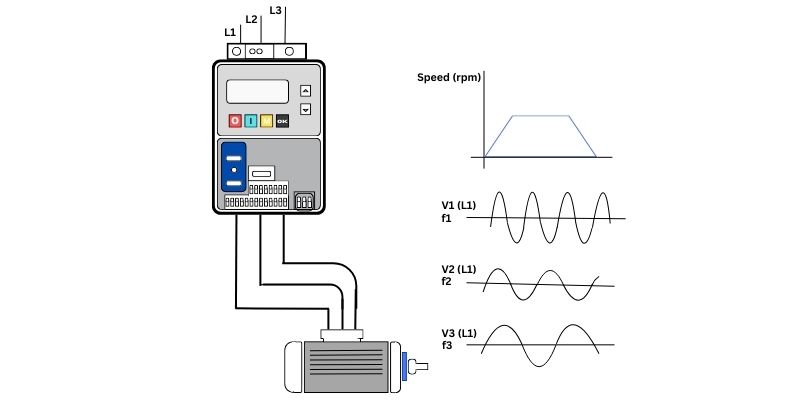
Namely, the variable speed control of an electric motor is primarily a matter of controlling the frequency and voltage which is supplied to the motor. This is normally done with the help of Variable Frequency Drive better known as VFD in short.
A VFD simply controls the frequency of the electrical supply, hence giving control of the speed of the motor. For an AC motor, the speed is determined by the formula:For an AC motor, the speed is determined by the formula:
Speed (RPM) = 120 × Frequency (Hz) / No.s of Poles
In this manner, with the help of varying the frequency the VFD is able to step up or step down the motor speed while not influencing the voltage as much thereby leading to a more efficient and stable performance. One of the advantages of this system is that it can achieve a high acceleration and low deceleration which in many cases is desirable when using the system.
Parts and Functions:
As mentioned above, variable speed electric motors are made up of the stator a stationary part of the motor including:
|
Parts |
Functions |
| Stator:
Rotor: Variable Frequency Drive (VFD): Bearings: Shaft: Cooling System: Feedback Sensors: Control Panel: Windings: Housing/Enclosure: |
Generates the magnetic field to drive the rotor. Interacts with the magnetic field to create motion and torque. Adjusts the motor’s speed by controlling frequency and voltage. Supports the rotor and reduces friction. Transmits rotational motion and torque to connected equipment. Removes excess heat to prevent overheating. Monitors speed, position, and performance for precise control. Allows operators to manage speed and operational settings. Creates the magnetic field inside the stator. Protects internal components and aids in heat dissipation. |
How to Increase Speed:
The following are some of the ways through which one can be able to raise the speed of a variable speed electric motor. One of the most often used techniques is to alter the rate of the electrical input signal controlling the speed of the motor. The second way is in modifying the number of poles in the winding of the motor and its possible effect on the speed characteristics. Moreover, there are more advanced ways of controlling the speed of the motor through employing of specialty control systems and software given below:
- Adjust Frequency via VFD: Increase the frequency supplied to the motor using a Variable Frequency Drive.
- Increase Voltage: Raise the voltage within the motor’s rated limits.
- Reduce Mechanical Load: Decrease the resistance or load on the motor.
- Use Gear Systems: Adjust gear ratios to increase output speed.
- Rewind Motor: Modify the motor’s windings with fewer turns for higher speed.
- Upgrade to a Higher Speed Motor: Replace with a motor designed for higher speeds.
- Improve Power Supply Quality: Ensure stable and clean power supply.
- Enhance Cooling: Upgrade cooling systems to prevent overheating.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep the motor well-maintained and lubricated.
- Optimize Control Settings: Fine tune VFD and control parameters for better speed performance.
Winding Types (Variable Speed Electric Motors):
Variable speed electric motors may be wound in different ways to realize various operational parameters. Some of the winding types are;
- Lap winding
- Wave winding
- Concentric winding
Each type has its benefits in the aspect of the amount of torque produced, power, size, and usable speed range. There are various types of winding, depending on the required application, and selecting the right one has a great impact on the best performance of the motor in any given application.
Operating Ways:
The variable speed electric motors can be controlled in a variety of ways depending on the application of the specific system. In an Open loop control system, it is possible to preset the motor’s speed so that it outputs depending on what is wanted.
Closed-loop control involves the use of a feedback system where sensors are used to detect the speed of the motor and timely modification is made accordingly.
One such technique to get rid of the external sensors is Sensorless control in which, the speed control is derived from the motor parameters.
Each of the operating methods has its benefits and the most suitable method is used depending on the requirements of the application.
Conclusion:
Variable speed electric motors are a pivotal component of today’s industrial and commercial applications and offer the best of both worlds, flexibility in speed and energy conservation. These motors’ working principles, parts, winding types, operating ways, and all other facts can be used by engineers and technicians to enhance their operation as per their numerous applications.
FAQs:
1. How does Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) control the speed of a variable speed electric motor?
A variable speed electric motor is controlled mainly through Variable Frequency Drive(VFD) through varying the frequency and voltage of power supplied to the electric motor. When it comes to the task demand or productivity it is possible to adjust the frequency of a motor and therefore run the motor at the appropriate speed which is needed.
2. What are the main constituents of a variable speed Electric motors?
They are stator, rotor, Variable Frequency Drive (VFD), bearings, shaft, cooling system, feedback sensors, control panel, windings and housing or enclosure. All the aforesaid parts have unique functions to perform so as the motor can run smoothly at different speeds.
3. Is it possible to make the speed of the electric motor increase by increasing the voltage of the supply?
Yes, it is acceptable to make changes to the voltages within the motors rated values and with a frequency of operation through VFD this can help increase the speed. But again one has to make sure that the volts should not go high than the motor voltage rating in a bid to cause damage.
4. What types of windings used in variable speed electric motors?
Variable speed electric motors can employ a range of windings for instance lap winding, wave winding as well as concentric winding. Each of them has different advantages as for the levels of torque, power, size and the range of speed for specific applications.
5. What are the Merits of using a sensor less control technique in variable speed electric motors?
The absence of sensors in driving the speed of the motor is the key to sensorless control method. This method also solves the problem of complexity by having an optimized system, and it also makes it cheaper, it is also believed to make it more reliable in the situation that maintaining sensors is difficult.

Pingback: AC Motor vs DC Motor: The Ultimate Showdown of Power and Performance - TechAnApple